Vitamin D Levels
Fewer than 3% of the US African American population is within our recommended range for vitamin D level, 40-60 ng/ml. 63% are below 20 ng/ml, putting them at risk for rickets and
osteomalacia
, as well as a host of other diseases.
The chart below shows the breakdown of vitamin D levels in children by race.
Black children and teens are most deficient in vitamin D, with 41% below 20 ng/ml. Nearly 100% of black and Hispanic children and teens are below 40 ng/ml. A
2014 study
by the Centers for Disease Control found that black and Hispanic kids have a 50% chance of developing diabetes, 10% more than the overall population.
Pregnancy
Preterm birth rates among African American women are 48% higher than the rate of all women (
source: March of Dimes). Rates of preeclampsia among African American women are approximately 50% higher than the rates among Caucasians over the past 30 years (
source: Breathett et al.). The chart below shows that 73% of black women of childbearing years in the US are below 20 ng/ml.
Since
early 2000
, Drs Carol Wagner and Bruce Hollis have been researching the effects of vitamin D on pregnancy and lactation.
In a time when this dosage was unheard of, they started giving study participants 4000 or 6000 vitamin D daily.
Through their research they have made some key observations - that pregnant women should be above 40 ng/ml to reduce the risk of preterm birth, and that lactating moms need 6400 IU/day to transfer the equivalent of 400 IU/day to their baby through breast milk.
In October 2015, researchers from GrassrootsHealth and Medical University of South Carolina published a paper,
Post-hoc analysis of vitamin D status and reduced risk of preterm birth in two vitamin D pregnancy cohorts compared with South Carolina March of Dimes 2009-2011 rates
,
which found
that there was a steady increase of gestation time (how long the baby stayed in the womb) correlating to the rise of 25(OH)D - but then reaching a plateau around 40 ng/ml.
This adds evidence to the effort to change the standard of practice for all OBs - with a goal of getting all pregnant women to a vitamin D level of at least 40 ng/ml.
A study done at Harvard Medical School, with lead investigator Hooman Mirzakhani, found that women who had vitamin D levels above 40 ng/ml by the end of pregnancy had no instances of preeclampsia, a condition that is prevalent in women with dark skin, but can be virtually eliminated by increasing vitamin D levels.
Diabetes and Heart Disease
What about diabetes? Heart disease? According to the
American Diabetes Association, 13.2% of all African Americans aged 20 or older have been diagnosed with diabetes and African Americans are 1.7 times more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes compared to non-Hispanic whites. According to
Close the Gap, an organization aiming to eliminate cardiovascular care disparities through outreach and education, African American men have a 70% higher risk and African American women have a 50% greater risk of developing
heart failure than white men and women between the ages of 45 and 64.
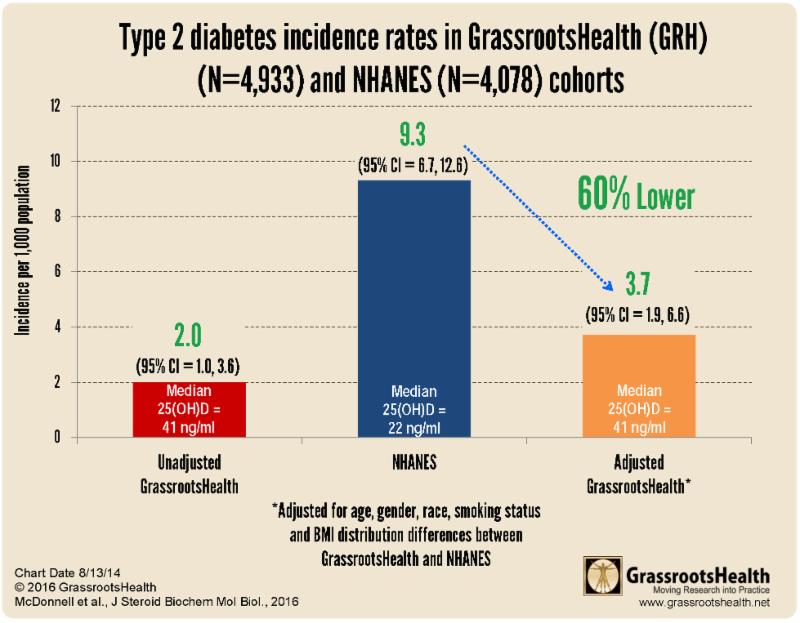
The chart below compares the D*action cohort to the US population, using NHANES data. The NHANES study population has an average vitamin D serum level of 22 ng/ml and an average incidence of diabetes is 9.3/1000 person-years. In comparison, the study population of D*action has an average vitamin D serum level of 41 ng/ml and a recorded diabetes incidence rate of 3.7/1000 person-years. Both groups have a similar BMI average.
|
Vitamin D Levels to Prevent Disease
48 vitamin D scientists have signed a
call to action
to bring attention to the appreciable associations between vitamin D insufficiency and many diseases - including rickets, osteomalacia, tuberculosis, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, type-1 diabetes, high blood pressure, increased heart failure, myopathy, breast and other cancers.
It is projected that the incidence of many of these diseases could be reduced by 20-50% or more, if the occurrence of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency were eradicated by increasing vitamin D intakes through increased UVB exposure, fortified foods or supplements. The appropriate intake of vitamin D required to effect a significant disease reduction depends on the individual's age, race, lifestyle, and latitude of residence. These scientists have stated that it is important to have vitamin D levels between 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) to prevent these diseases.
Increasing blood levels to this amount are safe and inexpensive.
$15 off in January with coupon code JAN17OFFER
|